Subject Preparation: ECG/EKG: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| ⚫ | |||
[[File:ECGleadplacement cropped.png|frameless|right| One Channel ECG/EKG, Recorded from the Chest]] |
[[File:ECGleadplacement cropped.png|frameless|right| One Channel ECG/EKG, Recorded from the Chest]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
'''Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) recording is used to identify and monitor cardiac activity in the MEG data.''' |
'''Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) recording is used to identify and monitor cardiac activity in the MEG data.''' |
||
There are many ways to monitor cardiac activity- some montages use one channel and some use two channels. Selection is usually based upon the reason(s) for measuring or recording cardiac events (e.g. heart rate monitoring, artifact detection and removal, etc.). Also, if the participant or patient population is uncomfortable with a chest montage, it is possible to create a similar triangle on the participant's arm. |
There are many ways to monitor cardiac activity- some montages use one channel and some use two channels. Selection is usually based upon the reason(s) for measuring or recording cardiac events (e.g. heart rate monitoring, artifact detection and removal, etc.). Also, if the participant or patient population is uncomfortable with a chest montage, it is possible to create a similar triangle on the participant's arm. |
||
Revision as of 16:12, 26 January 2022
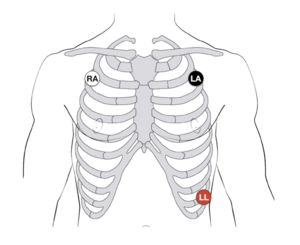
Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) Lead Placement
Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) recording is used to identify and monitor cardiac activity in the MEG data. There are many ways to monitor cardiac activity- some montages use one channel and some use two channels. Selection is usually based upon the reason(s) for measuring or recording cardiac events (e.g. heart rate monitoring, artifact detection and removal, etc.). Also, if the participant or patient population is uncomfortable with a chest montage, it is possible to create a similar triangle on the participant's arm.
Procedure:
- 1. Prepare the skin on the chest where electrodes will be placed:
- Abrade the skin with Nuprep.
- Use an alcohol wipe to remove the gritty residue.
- 2. If using pregelled Biopac electrodes, proceed to step 3. If using Ten/20 paste, carefully scoop into the electrode cup. Otherwise, press the electrodes onto the skin and apply electrolyte gel through the electrode opening with a syringe.
- 3. Using large EEG adhesive washers, place the electrodes firmly as follows:
- RA ('Right Arm') - just under the right clavicle.
- LA ('Left Arm') - just under the left clavicle (this will be the reference).
- LL ('Left Leg') - bottom left of ribcage.
- 4. Check the impedances using the Grass Impedance Meter:
- Plug the RA into jack# 1 and LL in jack# 2 and LA into jack# 3.
- Push the red ON button.
- The Electrode Selector should be at 1 or 2.
- ECG impedance should be < 50k ohms.
- Refer to section entitled “Electrode Impedance Meter Check” for more detailed information on reducing impedance.
- 5. Secure all electrodes with Transpore (medical) tape.
- If you require further assistance, please request technical assistance from MEG staff.
Electrode Types
BIOPAC Radiotranslucent Electrodes (#EL508)
- Disposable, radiotranslucent, pre-gelled electrodes with adhesive.
- Manufacturer Website
- Use with reusable radiotranslucent leads.

Gereonics Ag/AgCl Electrodes
- Reusable.
- Manufacturer Website
- Must be sent to Sterile Processing Services after each study.
- Rinse with distilled water to remove electrolyte paste or gel before sending to SPS. Water is available in a gallon jug under the subject preparation table and can be refilled from the Laboratory of Cardiac Energetics (B1D405) in the NMR Center.
Reducing Skin Impedances

Nuprep is a topical abrasive used for reducing skin impedance. It cleans the skin by removing any natural or applied oil, lotions and/or dead skin. Remove with water.
- Insert the wooden end of a cotton swab through the opening of the electrode to push hair aside (in one direction) until the skin is clearly visible.
- If the hair is long, lift up the electrode a little and let it down again while moving back the swab to grab a new bunch of hair (this will prevent the hair from slipping back).
- Dip the swab into the Nuprep and insert through the electrode opening.
- Twirl the swab against the skin using the thumb and index finger.
Applying Electrolyte

Ten/20 Conductive Cream is an opaque white, water soluble electrolyte substance used as a conductive and/or fixing/adhering medium to attach electrodes. Removed with warm water.
- *If using Ten/20 - scoop paste into a cup electrode (this paste is too thick to squirt from a syringe).
- Press firmly on the skin.
- *If using a liquid electrolyte like Electrogel, Elifix or Abralyt
- Fill a syringe with the solution.
- Squirt into the middle of each electrode opening.
- *Completely fill the electrode space (the space from the skin to the electrode) with cream / paste so that there are no air pockets and the electrolyte makes good contact with the skin.
If the electrodes are closely spaced, be careful to avoid electrical bridging. This happens when electrolyte from adjacent electrodes pools together. To avoid this, draw back the syringe concurrently to prevent electrolyte from swelling underneath the electrode rim and bridging to the adjacent electrodes. When using Ten/20 do not allow the paste from adjacent electrodes to touch
NOTE: You are not required to use Ten/20 paste, however care should be take when selecting an electrolyte solution/paste for use in MEG. Many solutions, if not prepared specifically for use in MEG, may have magnetic contaminants.
- CTF released the following advisement:
 EEG Gel Magnetic Contaminants
EEG Gel Magnetic Contaminants
Electrode Impedance Meter Check

The Grass S88 Impedance Meter measures AC impedance (resistance and capacitance). An impedance check should be performed on all electrodes used for EEG or EMG. When two or more electrodes are plugged into the electrode switch positions, all electrodes except the one selected electrode being measured are connected together and provide the reference for the one being measured.
- 1. The Electrode Selector Switch should be at Jack position 1 or 2.
- 2. Plug the ground electrode into electrode Jack 1 position.
- 3. Plug the other electrodes into the Jack (2, 3, 4, etc) positions in a systematic manner one at a time.
- 4. Press the Red ON Button to activate the impedance check. The power will automatically shutoff after approximately 2 minutes. (There is no OFF button.)
- 5. If the impedance is too high - take a cotton tip swab dipped in Nuprep (or other skin prep) and twirl against the skin until impedance is at an appropriate level. Then re-insert Elifix electrolyte.
- Impedance Recommendations
EEG Electrodes ≤ 5Kohms EMG/EOG/ECG ≤ 50Kohms
- *If the electrode impedance exceeds 199.9K ohm, a “1” will appear in the left display window with all other digits blanked out indicating the impedance is too high. Remove the electrode, abrade the skin with Nuprep again, then re-apply the electrolyte paste and check the impedance again.
- 6. After checking the impedance of each electrode plug the electrode into the appropriate electrode jack.
MEG DSQ 3500 Amplifier Setup

Located inside the MSR on the table near the MEG machine. The DSQ 3500 Amplifier has inputs for:
- Fiducial Coils - Nasion, Left Ear, Right Ear, Inion(unused) and Vertex(unused)
- Ground Jack - labeled 'Z'
- Reference Jack - labeled 'REF'
- Unipolar channels (21 jacks) - unipolar channels which measure the difference between an electrode and a common reference channel. The reference channel is common to all of the EEG unipolar channels
- Bipolar Channels (8 jacks) - bipolar channels which measure the potential difference between two individual electrodes. These channels are labelled A - G on the jackbox, however, the channels are numbers 56 to 62 in the ACQ parameters
- ZIF Connector/Jig Connector - connection for the EEG EasyCap System which can accommodate up to 56 electrode positions
Please note: There is a Static Dissipation Button which you must touch before touching anything else on the amplifier and before plugging any electrodes into the amplifier.
- If Using a One Channel Bipolar ECG/EKG montage (three leads):
- Plug the electrodes into a bipolar channel.
Note: if recording only ECG/EKG (no EEG or EOG) you will still need to have a ground electrode. Plug in the reference to the ground.
Post-Study Disinfection
If you are using disposable electrodes (i.e. Biopac), discard the electrode and clean the electrode lead with alcohol.
If you are using reusable electrodes, they must be sent to Sterile Processing Services for sterilization.
Procedure:
1. Clean electrolyte paste or gel from the electrodes using only distilled water. Water is available in a jug underneath the subject preparation table and can be filled at the Laboratory of Cardiac Energetics (B1D405) in the NMR Center.
2. Place rinsed electrodes in the special two-part ziploc bags provided in the lab (on the left side of the supply cabinet. The electrodes should be on the interior pocket, with the leads tucked in the exterior pocket.
3. Fill out the sterilization request form, according to the following template. It is important to mark the following instructions on the form so that the electrodes are not damaged during handling:
- STERRAD
- Distilled/Deionized water only
- Keep out of direct light when not in use
- If you notice that the electrodes are returned in poor condition, please let the lab manager know as soon as possible so SPS can be notified.
4. Place the electrode baggie inside the amber three-part transport container, with the request form on top. You can leave it on Anna's desk for collection.
5. Contact SPS to notify them that the MEG Core has electrodes to pick up. They will usually send someone within the next 24 hours.
- Sterile Processing Services: 301.402.2853
- B.B. Avila: 301.435.4096